| [ Team LiB ] |
|
Recipe 14.1 Dynamically Link SQL Server Tables at Runtime14.1.1 ProblemYour Access SQL Server database uses linked tables and views in SQL Server. You have set up security and permissions in SQL Server and want to make sure that each user's linked tables are attached under their own permissions, not another user's permissions. In addition, you don't want the users to be prompted for an additional login ID and password each time they use a table. 14.1.2 SolutionIf you link SQL Server tables from an Access database using the File Get External Data menu commands, you will be prompted to use or create a Data Source Name (DSN). The main drawback to DSNs is that they need to be installed on every user's machine. A better solution is to use VBA code to link or relink tables. You can supply connection information in the Connection string without having to create a DSN. This technique uses DAO to create new TableDef objects in each database when the application starts up. The startup form for the application has a dialog where the user can supply a login and password to be used to connect to SQL Server. The list of table names is stored in a local Access ( Jet) database. To add this technique to your application, follow these steps:
Figure 14-1. tblSQLTables has entries to link to the tables in the Northwind database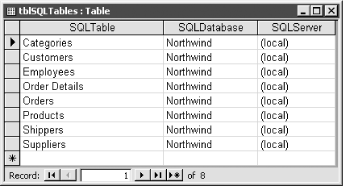
Figure 14-2. The startup form allows users to supply login information for the linked tables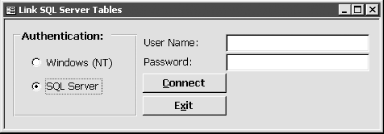
Figure 14-3. Setting a reference to the DAO object library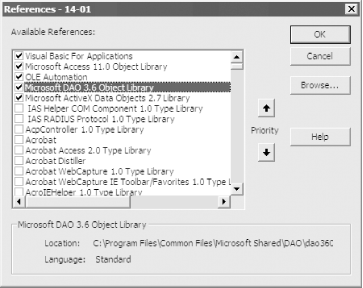
The completed application is shown in 14-01.MDB, which contains the local table used to store data about the tables that are linked from the Northwind SQL Server database. A startup form contains the relinking code. 14.1.3 DiscussionThe first step in linking SQL Server tables is to build the ODBC Connection string that will be used to link the tables. You could use a DSN, but you'd have to create the DSN if it didn't exist. We find it easier to simply build a dynamic string with all the required information. The first part of the string contains connection information that will be the same for every table: Select Case Me.optAuthentication
' Windows/NT login
Case 1
strConnect = "ODBC;Driver={SQL Server};Trusted_Connection=Yes;"
' SQL Server login
Case 2
strConnect = "ODBC;Driver={SQL Server};UID=" _
& Me.txtUser & ";PWD=" & Me.txtPwd & ";"
End Select
The next step is to delete any old linked SQL Server tables by calling the DeleteLinks procedure: Call DeleteLinks The DeleteLinks procedure walks through the current database's TableDefs collection, deleting only linked ODBC tables. Here's the complete listing: Private Sub DeleteLinks( )
' Delete any leftover linked tables from a previous session.
Dim tdf As DAO.TableDef
On Error GoTo HandleErr
For Each tdf In CurrentDb.TableDefs
With tdf
' Delete only SQL Server tables.
If (.Attributes And dbAttachedODBC) = dbAttachedODBC Then
CurrentDb.Execute "DROP TABLE [" & tdf.Name & "]"
End If
End With
Next tdf
ExitHere:
Set tdf = Nothing
Exit Sub
HandleErr:
MsgBox Err & ": " & Err.Description, , "Error in DeleteLinks( )"
Resume ExitHere
Resume
End Sub
The next step is to create a recordset that lists the table names, the SQL Server database name, and the SQL Server itself. If no tables are listed, the procedure terminates. This portion of code is as follows: Set db = CurrentDb
Set rst = db.OpenRecordset("tblSQLTables", dbOpenSnapshot)
If rst.EOF Then
strMsg = "There are no tables listed in tblSQLTables."
GoTo ExitHere
End If
Next, walk through the recordset, creating a new TableDef object for each table listed. The Connect property is set to the base connection string, with the server and database name concatenated. The TableDef object's SourceTableName is set to the table name in the database, and the TableDef object is appended to the TableDefs collection. This portion of code resides in the following Do Until loop: Do Until rst.EOF
strServer = rst!SQLServer
strDB = rst!SQLDatabase
strTable = rst!SQLTable
' Create a new TableDef object.
Set tdf = db.CreateTableDef(strTable)
' Set the Connect property to establish the link.
tdf.Connect = strConnect & _
"Server=" & strServer & _
";Database=" & strDB & ";"
tdf.SourceTableName = strTable
' Append to the database's TableDefs collection.
db.TableDefs.Append tdf
rst.MoveNext
Loop
Once the TableDefs are appended, the cleanup code runs and the user is notified that the tables have been successfully linked: strMsg = "Tables linked successfully."
rst.Close
Set rst = Nothing
Set tdf = Nothing
Set db = Nothing
ExitHere:
MsgBox strMsg, , "Link SQL Tables"
Exit Sub
The
technique discussed here for relinking tables works well in any
version of SQL Server and is not specific to any version of Access.
Any time you use DAO in your code, you need to open the Tools
|
| [ Team LiB ] |
|