| [ Team LiB ] |
|
Recipe 7.6 Pass a Variable Number of Parameters to a Procedure7.6.1 ProblemYou need a procedure that will work on a list of items, and you don't know ahead of time how many there will be. You know that VBA will allow you to use optional parameters, but this requires you to know exactly how many items you might ever need to pass, and in your case, it's impossible to predict that value. How can you accomplish this? 7.6.2 SolutionYou have two choices in solving this problem: you can pass an array as a parameter, or you can pass a comma-delimited list, which Access will convert into an array for you. An array (an ordered list of items) must contain a single data type. By using the variant data type, though, you can pass a list of varying types into your procedure. This solution demonstrates both these techniques. From 07-06.MDB, load the module basArrays in design mode and do the following:
Figure 7-9. TestUCase with five strings converted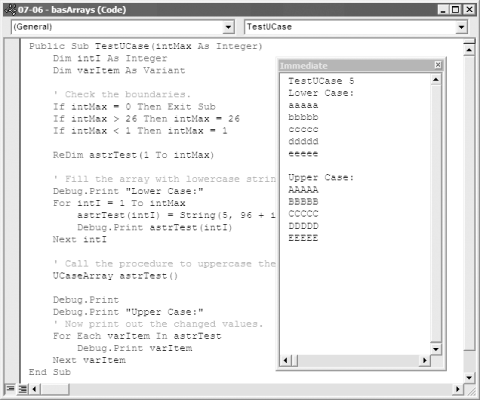
Figure 7-10. TestSum summing 15 values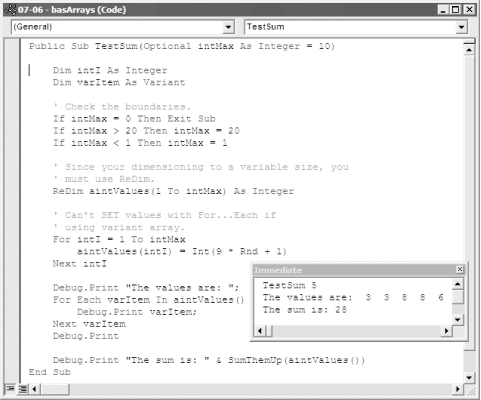
Both UCaseArray and SumThemUp accept a variant as a parameter. This variant variable can hold either a single value or an array of values. From the calling end, you can pass either a variant or an actual array of values. To send an array as a parameter, you must add the trailing ( ) characters, indicating to Access that the variable represents an array. Therefore, to pass the array named aintValues to SumThemUp, call the function like this, making sure to include the ( ) in the array name: varSum = SumThemUp(aintValues( )) To receive a parameter that is an array, the procedure declaration can include the parentheses: Public Function SumThemUp (aintValues( ) As Integer) As Variant in which case you can pass only an array. You can also declare it like this: Public Function SumThemUp (varValues As Variant) As Variant in which case you can pass it either a single variant value or an array of values. Once the procedure has received the array, it needs a way to loop through all the elements of the array. Access provides two methods for walking the array: looping through the items either with a For...Next loop (by index number), or with a For Each...Next loop (without using the index). UCaseArray uses the first method to loop through all the members of its array, and SumThemUp uses the second. To loop through the elements of an array by number, you must know the bounds of the array; i.e., the lowest and highest element numbers. Access provides two functions, LBound and UBound, to retrieve the lowest and highest element numbers. UCaseArray includes code like this: For intI = LBound(varValues) To UBound(varValues) varValues(intI) = UCase(varValues(intI)) Next intI This code loops through all the elements in the array, no matter what the starting and ending items are. In Basic, you can declare an array with any positive integer as its start and end points. For example, in this expression: Dim avarArray(13 To 97) as Integer you'd need to loop from 13 to 97 to access each element of the array. The LBound and UBound functions make it possible for generic routines to loop through all the elements of an array, even though they don't know ahead of time how many elements there will be. The UCaseArray procedure is quite simple: once it determines that the input value is actually an array (using the IsArray function), it loops through all the elements of the passed-in array, converting each to uppercase. The array is passed by reference, using the ByRef keyword, which means that the modified array is returned to the calling procedure. The code for UCaseArray is: Public Sub UCaseArray(ByRef varValues As Variant)
' Convert the entire passed-in array to uppercase.
Dim intI As Integer
If IsArray(varValues) Then
For intI = LBound(varValues) To UBound(varValues)
varValues(intI) = UCase(varValues(intI))
Next intI
Else
varValues = UCase(varValues)
End If
End Sub
The SumThemUp function is no more complex. It uses the For Each...Next syntax to walk through all the elements of the array, maintaining a running sum as it loops. In this case, the variant variable varItem takes on the value of each element of the array as it loops through the items, and adds its value to varSum. The source code for SumThemUp is: Public Function SumThemUp(varValues As Variant) As Variant
' Find the sum of the values passed in.
Dim varItem As Variant
Dim varSum As Variant
varSum = 0
If IsArray(varValues) Then
For Each varItem In varValues
varSum = varSum + varItem
Next varItem
Else
varSum = varValues
End If
SumThemUp = varSum
End Function
Passing a list that Access converts to an array for you is no more difficult. To use this technique, you must declare your procedure's formal parameters so that the list of values is the last parameter the procedure expects to receive. Use the ParamArray keyword to indicate that you want to treat an incoming list as an array, and declare your array parameter as an array of variants: Public Function MinValue(ParamArray varValues( ) As Variant) As Variant Once inside the procedure, you can treat the array parameter like any other array. That is, you can either loop from LBound to UBound for the array, or use a For Each...Next loop to visit each element. 7.6.3 DiscussionTo use this method effectively, be aware that unless told otherwise, Access always creates arrays with the first element numbered 0. Some programmers insist on starting all arrays with 1 and so use the Option Base 1 statement in their modules' Declarations areas. Others are happy with 0 as their starting point, and some leave the option base setting at 0 (its default) but disregard the element numbered 0. You must never assume anything about the lower or upper bounds on arrays, or sooner or later generic routines won't work. If you're writing code that will be called by other programmers, you need to be aware of these variations on the normal usage. If you decide to use the For Each...Next syntax to access all of the elements of an array, both the variable you use to loop through the elements and the array itself must be variants. In addition, note that you cannot set the values of items in an array using the For Each...Next syntax; it only allows you to retrieve the values from the array. If you want to loop through an array to set its values, you must use the standard For...Next syntax, using a numeric value as the loop counter. In Access 2000 and later, you can use an array as the return value for a function. Thus, you could rewrite the UCaseArray procedure as follows: Public Function UCaseArrayFunc(ByVal varValues As Variant) As String( )
' Convert the entire passed in array to upper case.
Dim intI As Integer
Dim astrWorking( ) As String
If IsArray(varValues) Then
ReDim astrWorking(LBound(varValues) To UBound(varValues))
For intI = LBound(varValues) To UBound(varValues)
astrWorking(intI) = CStr(UCase(varValues(intI)))
Next intI
UCaseArrayFunc = astrWorking
End If
End Function
The advantage of this technique is that the function returns a second array and the original array, varValues, is not modified. Unlike the first example, UCaseArray, the array is passed ByVal, which means that UCaseArrayFunc works with a copy of the original array. Any modifications occurring in UCaseArrayFunc will affect only this copy, leaving the original array in the calling procedure unchanged. |
| [ Team LiB ] |
|