|
|
< Day Day Up > |
|
6.3 Word Spacing and Letter SpacingNow that we've dealt with alignment, let's look at manipulating word and letter spacing. As usual, these properties have some unintuitive issues. 6.3.1 Word Spacing
The word-spacing property accepts a positive or negative length. This length is added to the standard space between words. In effect, word-spacing is used to modify inter-word spacing. Therefore, the default value of normal is the same as setting a value of zero (0). If you supply a positive length value, then the space between words will increase. Setting a negative value for word-spacing brings words closer together: p.spread {word-spacing: 0.5em;}
p.tight {word-spacing: -0.5em;}
p.base {word-spacing: normal;}
p.norm {word-spacing: 0;}
<p class="spread">The spaces between words in this paragraph will be increased
by 0.5em.</p>
<p class="tight">The spaces between words in this paragraph will be decreased
by 0.5em.</p>
<p class="base">The spaces between words in this paragraph will be normal.</p>
<p class="norm">The spaces between words in this paragraph will be normal.</p>
Manipulating these settings has the effect shown in Figure 6-19. Figure 6-19. Changing the space between words So far, I haven't actually given you a precise definition of what a "word" is. In the simplest CSS terms, a "word" is any string of nonwhitespace characters that is surrounded by whitespace of some kind. This definition has no real semantic meaning—it simply assumes that a document contains words surrounded by one or more whitespace characters. A CSS-aware user agent cannot be expected to decide what is a valid word in a given language and what isn't. This definition, such as it is, means word-spacing is unlikely to work in any languages that employ pictographs, or non-Roman writing styles. The property allows you to create very unreadable documents, as Figure 6-20 makes clear. Use word-spacing with care. Figure 6-20. Really wide word spacing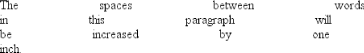 6.3.2 Letter Spacing
Many of the same issues you encountered with word-spacing also occur with letter-spacing. The only real difference between the two is that letter-spacing modifies the space between characters, or letters. As with the word-spacing property, the permitted values of letter-spacing include any length. The default keyword is normal (making it the same as letter-spacing: 0). Any length value you enter will increase or decrease the space between letters by that amount. Figure 6-21 shows the results of the following markup: p {letter-spacing: 0;} /* identical to 'normal' */
p.spacious {letter-spacing: 0.25em;}
p.tight {letter-spacing: -0.25em;}
<p>The letters in this paragraph are spaced as normal.</p>
<p class="spacious">The letters in this paragraph are spread out a bit.</p>
<p class="tight">The letters in this paragraph are a bit smashed together.</p>
Figure 6-21. Various kinds of letter spacing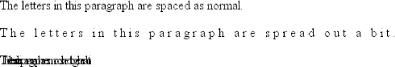 Using letter-spacing to increase emphasis is a time-honored technique. You might write the following declaration and get an effect like the one shown in Figure 6-22: strong {letter-spacing: 0.2em;}
<p>This paragraph contains <strong>strongly emphasized text</strong>
that is spread out for extra emphasis.</p>
Figure 6-22. Using letter-spacing to increase emphasis6.3.3 Spacing and AlignmentBoth word-spacing and letter-spacing may be influenced by the value of the property text-align. If an element is justified, the spaces between letters and words are altered to fit the text along the full width of the line. This may in turn alter the spacing declared by the author with word-spacing or letter-spacing. CSS does not specify how the spacing should be calculated; so user agents simply fill it in. As usual, the child of an element inherits the computed value of that element. You cannot define a scaling factor for word-spacing or letter-spacing to be inherited in place of the computed value (as is the case with line-height). As a result, you may run into problems such as those shown in Figure 6-23: p {letter-spacing: 0.25em; font-size: 20px;}
small {font-size: 50%;}
<p>This spacious paragraph features <small>tiny text that is just
as spacious</small>, even though the author probably wanted the
spacing to be in proportion to the size of the text.</p>
Figure 6-23. Inherited letter spacing The only way to achieve letter spacing that's in proportion to the size of the text is to set it explicitly, as follows: p {letter-spacing: 0.25em;}
small {font-size: 50%; letter-spacing: 0.25em;}
|
|
|
< Day Day Up > |
|