|
|
|
13.44 <stdexcept>The <stdexcept> header defines several standard exception classes. (Refer to <exception> for the base exception class.) Figure 13-24 shows all the exception classes in the standard library, including a few that are declared in other headers. Note that the standard library has very few places that throw exceptions. The exceptions in <stdexcept> are available primarily for your use. Figure 13-24. All the standard exception classes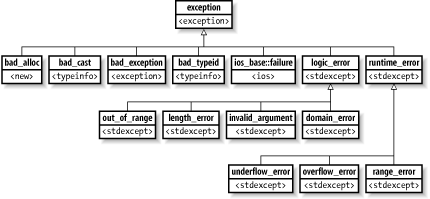 See Chapter 3 for more information about throw expressions and Chapter 4 for information about handling exceptions with try statements.
The domain_error class is used to report domain errors, that is, arguments to functions that are outside the valid domain for input to the functions. For example, a function that converts a color from the Hue, Saturation, Lightness colorspace to the Red, Green, Blue colorspace might require a Saturation in the range [0.0, 1.0] and throw domain_error for any other value. See Alsologic_error class
The invalid_argument class is thrown to report invalid arguments to functions. Specific kinds of invalid arguments are covered by the other logic errors; use invalid_argument for any other situations. For example, constructing a bitset from a string throws invalid_argument if any character is other than '0' or '1'. See Alsologic_error class
The length_error class is used to attempt to set or change the size of an object that exceeds the maximum size. For example, the string class throws length_error if you attempt to create a string longer than max_size( ) characters. See Alsologic_error class
The logic_error class is a base class for logic-error exceptions. A logic error is a violation of the preconditions or other requirements for a function. See Alsodomain_error class, invalid_argument class, length_error class, out_of_range class, runtime_error class
The out_of_range class is used when an index or similar value is out of its expected or allowed range. For example, the at member (of deque, string, and vector) throws out_of_range if the index is invalid. See Alsologic_error class
The overflow_error class can be used for arithmetic overflow. For example, bitset::to_ulong throws overflow_error if the arithmetic value of the bitset exceeds the maximum value of an unsigned long.
Note that overflow in most arithmetic expressions has undefined behavior; an implementation might throw overflow_error, but there is no guarantee that it will throw this or any other exception. See Alsoruntime_error class
The range_error class can be used when a function's results would fall outside its valid range. Note that the <cmath> functions do not throw any exceptions, but a third-party math library might throw range_error for, say, computing a power that exceeds the limits of its return type. See Alsoruntime_error class
The runtime_error class is the base class for runtime errors, which are errors that cannot reasonably be detected by a static analysis of the code but can be revealed only at runtime. See Alsooverflow_error class, range_error class, underflow_error class
The underflow_error class can be used for arithmetic underflow. Note that underflow in most arithmetic expressions has undefined behavior; an implementation might throw underflow_error, but there is no guarantee that it will throw this or any other exception. See Alsoruntime_error class |
|
|
|