|
|
11.1 Creating HTML StylesHTML styles are applied and managed by
using the HTML Styles panel, shown in Figure 11-1. Open it using Window Figure 11-1. The HTML Styles panel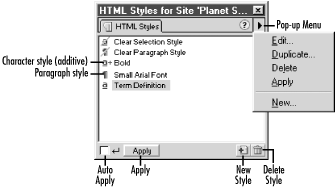 Unlike styles that appear in the CSS Styles panel, which are specific to the current document, styles stored in the HTML Styles panel are available to all documents in your site. This feature makes HTML styles easier to apply locally, whereas CSS styles are easier to manage globally. HTML styles cannot contain text or other content—they are used strictly for formatting. To insert, for example, a formatted copyright notice, you can use the History panel to record a "macro" command. You can also use the Assets panel to store favorite images, colors, and other assets. Although there is no text category in the Assets panel, you can use the Library category to hold commonly needed chunks of HTML (which can include text). Library assets have the advantage of being linked so that, unlike HTML styles, all instances of a library item update if the original item changes. 11.1.1 Character Formatting Versus Paragraph FormattingTwo default "styles"—Clear Selection Style and Clear Paragraph Style—always appear at the top of the HTML Styles panel. These pseudo-styles are used to remove existing formatting from either a character span or an entire paragraph. Character formatting can be applied to any span of characters; paragraph formatting affects an entire paragraph. For example, bold formatting can be applied on a character-by-character basis—a single word or even a single character could be bolded while leaving the rest of a paragraph unbolded. But certain attributes, such as alignment, make sense only when applied to an entire paragraph (i.e., the same paragraph can't have text that is both centered and left-aligned; all the text must share the same alignment). Because HTML defines both character-level tags (such as <i> and <b>) and paragraph-level tags (such as <p> and <h1>), Dreamweaver supports both character-level and paragraph-level HTML styles. 11.1.2 Defining an HTML Style's AttributesCreate a new HTML style by clicking the New Style icon in the HTML Styles panel, as indicated in Figure 11-1. Clicking this icon opens the Define HTML Style dialog box, shown in Figure 11-2, where you'll assign the text formatting for the style. Table 11-1 explains the Define HTML Styles dialog box options.
Because styles are sorted alphabetically in the HTML Styles panel, you can group styles in the list by naming them appropriately. Figure 11-2. The Define HTML Style dialog box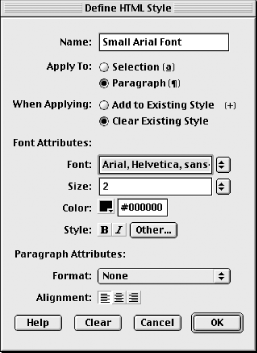
There are several other ways to open the Define HTML Style dialog box:
When creating a new style, attributes of the currently selected text are used to fill in the attributes in the Define HTML Style dialog box. You can use the Clear button in this dialog box to reset the style attributes to their default values. |
|
|