| [ Team LiB ] |
|
A.3 Scalability Patterns
GoalCache remote data as it is generated. Participants
InteractionsThe subscriber retrieves data from the publisher either when it has changed or at some predefined interval. The subscriber processes the data and updates all appropriate models. When requests are received, the view translates current model data into a format suitable for the user. NotesThe most effective use of this pattern is when a single subscriber downloads dynamic data and uses it to generate static HTML pages on each web server. It is also useful in situations where multiple web servers use separate data models that must be kept up to date.
GoalMinimize repeated page generation by caching dynamic pages when they are generated (Figure A-13). Figure A-13. Classes in the Caching Filter pattern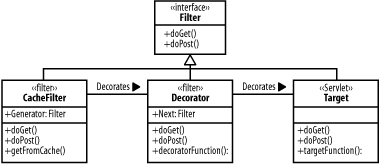 Participants
InteractionsThe cache filter intercepts all requests destined for target and determines if the page has been cached. If it is cached, data is returned from the cache. If not, the remaining decorators in the chain and the target are executed to generate the page, and the results are cached. NotesThe caching filter is a variation of the decorator pattern. To ease implementation of filters such as the caching filter, the servlet API allows you to decorate the HTTPServletResponse object in order to store the results of request processing.
GoalDecrease costs of instantiating and maintaining large objects using a pool of pre-generated objects (Figure A-15). Figure A-15. Classes in the Resource Pool pattern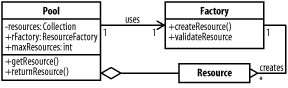 Participants
InteractionsThe client requests objects from the pool, which returns a resource if one is available. If no resources are available, but the pool is not at capacity, a new instance is generated using the factory. If all resources are loaned out, the client waits until one becomes available. When the client has finished using the resource, it returns it to the pool, which uses the factory to validate the returned resource. NotesA resource pool can easily be implemented based on the Java collections APIs. |
| [ Team LiB ] |
|