

|
|
11.7 Boxing and Unboxing TypesBoxing and unboxing are the processes that enable value types (e.g., integers) to be treated as reference types (objects). The value is "boxed" inside an Object and subsequently "unboxed" back to a value type. It is this process that allowed us to call the ToString() method on the integer in Example 11-4. (You will see additional uses for boxing and unboxing in Chapter 16.) 11.7.1 Boxing Is ImplicitBoxing is an implicit conversion of a value type to the type Object. Boxing a value allocates an instance of Object and copies the value into the new object instance, as shown in Figure 11-4. Figure 11-4. Boxing value types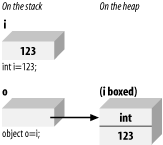 Boxing is implicit when you provide a value type where a reference is expected. The compiler notices that you've provided a value type and silently boxes it within an object. You can, of course, first cast the value type to a reference type, as in the following: int myIntegerValue = 5; object myObject = myIntegerValue; // cast to an object myObject.toString(); This is not necessary, however, as the compiler boxes the value for you silently and with no action on your part: int myIntegerValue = 5; myIntegerValue.toString(); // myIntegerValue is boxed 11.7.2 Unboxing Must Be ExplicitTo return the boxed object back to a value type, you must explicitly unbox it. For the unboxing to succeed, the object being unboxed must really be of the type you indicate when you unbox it. You should accomplish unboxing in two steps:
Example 11-5 illustrates boxing and unboxing. Example 11-5. Boxing and unboxingusing System;
public class UnboxingTest
{
public static void Main()
{
int myIntegerVariable = 123;
//Boxing
object myObjectVariable = myIntegerVariable;
Console.WriteLine("myObjectVariable: {0}",
myObjectVariable.ToString());
// unboxing (must be explicit)
int anotherIntegerVaraible = (int) myObjectVariable;
Console.WriteLine("anotherIntegerVariable: {0}",
anotherIntegerVariable);
}
}
Output:
myObjectVariable: 123
anotherIntegerVariable: 123
Figure 11-5 illustrates unboxing. Figure 11-5. Unboxing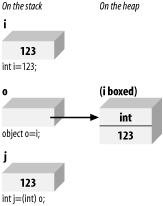 Example 11-5 creates an integer myIntegerVariable and implicitly boxes it when it is assigned to the object myObjectVariable; then, to exercise the newly boxed object, its value is displayed by calling toString(). The object is then explicitly unboxed and assigned to a new integer variable, anotherIntegerVariable, whose value is displayed to show that the value has been preserved.
|

|
|